Seguimento Europa - 2018
- Thread starter luismeteo3
- Data de início
-
O novo portal está no ar! Novos meteogramas, cartas, e mais. Mais informações neste tópico
Seguimento Meteorológico: Litoral Norte | Interior Norte e Centro | Litoral Centro | Sul | Açores e Madeira | Livre
Previsões: Curto e médio prazo: até 2 semanas | Longo prazo: mensal e sazonal (Regras e links úteis nos 1ºs posts)
Facebook | Avisos IPMA/Alertas ANEPC
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
http://www.estofex.org/
Mesoscale Discussion
Valid: Fri 28 Sep 2018 09:00 to Fri 28 Sep 2018 21:00 UTC
Issued: Fri 28 Sep 2018 09:01
Forecaster: ESTOFEX
This is a Mesoscale Discussions issued for a cyclone
that is primarily driven by convection, issued twice daily before 9,
and 21 UTC until the cyclone dissipates or becomes extratropical. This
Mesocale Discussion is not an official producat and does not substitute
any warnings from National Meteorological Services. We welcome any
feedback at [email protected].
System: 2018M02
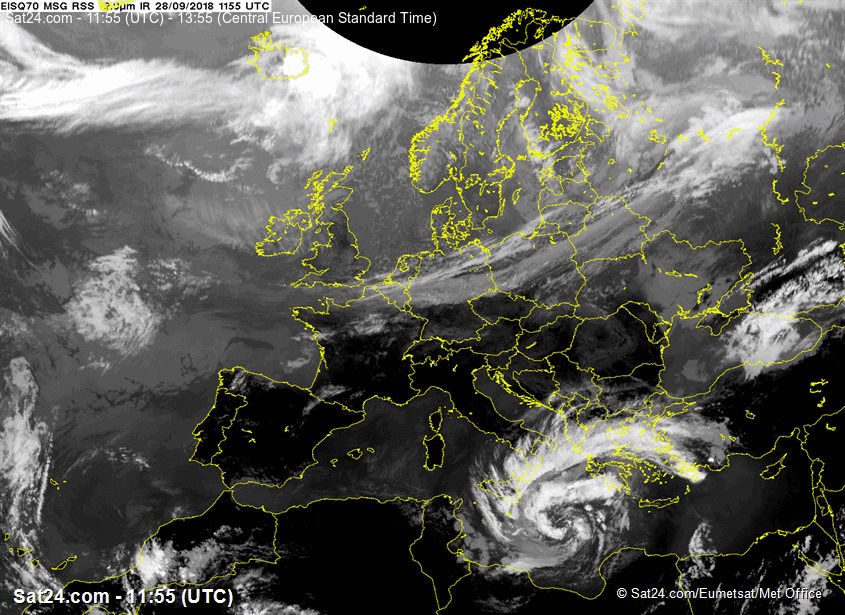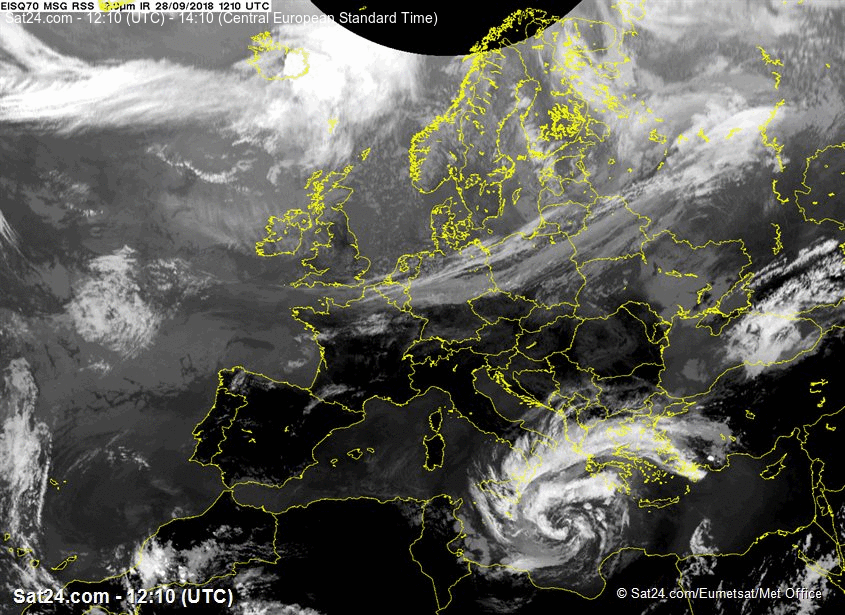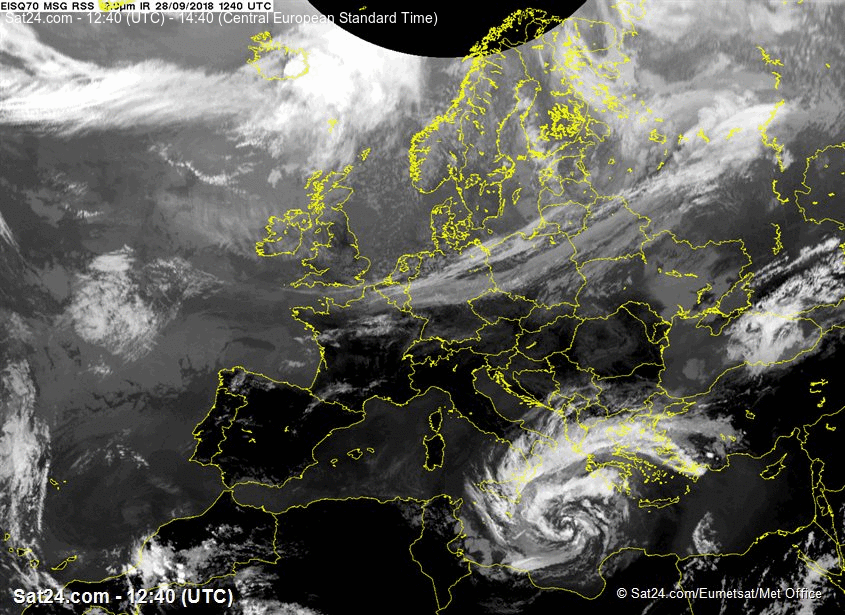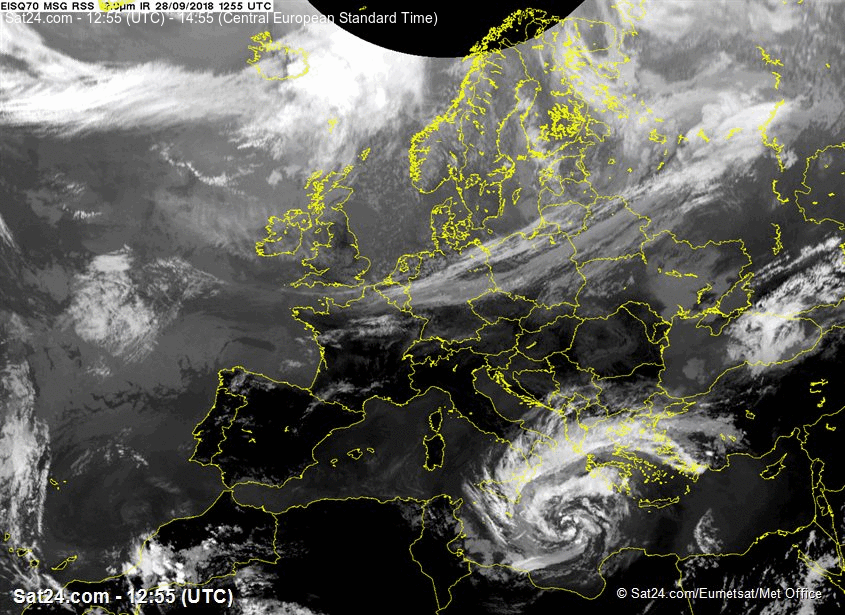
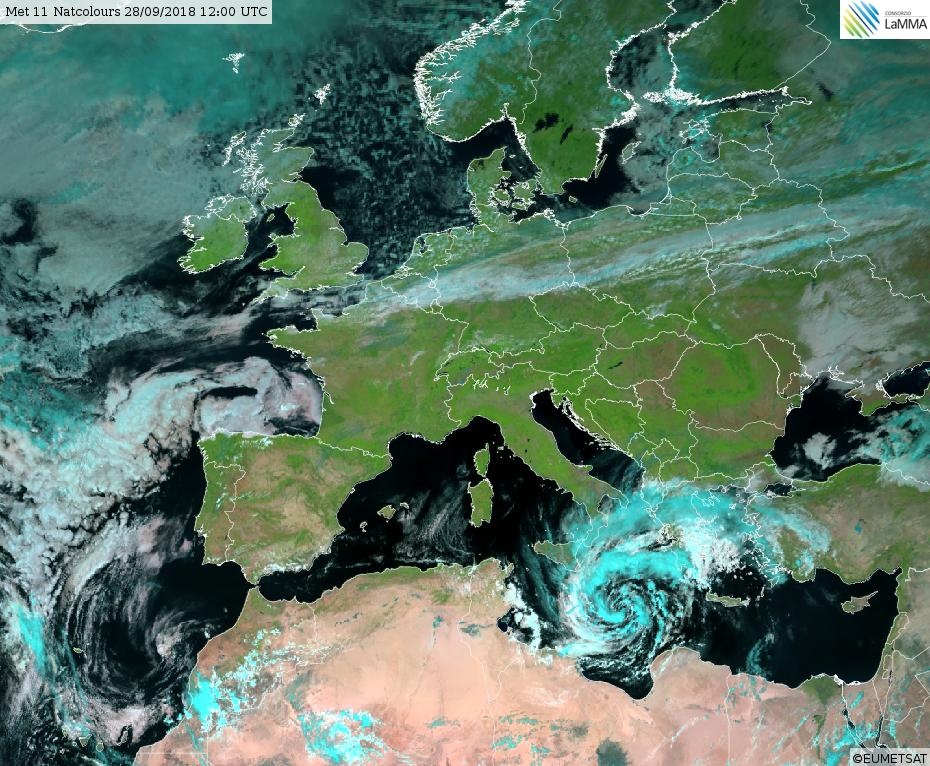
At 28 SEP 0600UTC the storm centre was located near 34.8N and 18.7E
Estimated minimum pressure: 995 mb.
Maximum sustained winds: 28 m/s (55 kt, 100 km/h).
Maximum gusts: 35 m/s (70 kt, 125 km/h).
ANALYSIS
Overnight,
the cyclone has organized and deepened, while drifting northward. Cloud
bands are spiralling around the intensified vortex, although a tight
inner circulation has not (yet) developed. A subjective Hebert-Poteat
technique estimate yields T numbers between 3.0 and 3.5 at 06 UTC,
supporting a minimum pressure of near 995 mb and maximum sustained winds
near 28 m/s.
FORECAST
Models are in agreement that the
cyclone should move only very slowly during the next 12 hours, before
accelerating east-northeastward towards the Peloponnese, as an upper
left trough approaches from the northwest. The greastest uncertainty in
the forecast is the extent of interaction with the mountainous region of
the Peloponnese: ICON and UKMO predicting the greatest interaction and
strongest weakening, whereas ECMWF and ARPEGE continue feature a more
southerly track with less influence on the inner core. The new track and
intensity forecast are a blend of these different solutions. The track
has been adjusted slightly to the south, and is quicker after 36 hours.
The forecast takes the cyclone into Northwestern Anatolia on Sunday
evening, upon which the cyclone will weaken rapidly.
The cyclone
is predicted to intensify somewhat more prior to landfall the
Peloponnese as suggsted by UKMO and ARPEGE, before moderate weakening
occurs. As said, the intensity forecast after 36 hours is strongly
dependent on the level of interaction with terrain and therefore rather
uncertain.
The primary hazard of the cyclone is expected to be very
heavy precipitation. Amounts of 200-300 mm can be expected on Saturday
and Sunday across the Peloponnese, 125-250 mm over Attica, Eastern
Central Greece (including Euboia) and the Cyclades, and 50–125 mm over
southern Crete, Western Anatolia, the North Aegean Islands and
Dodecanese Islands. In addition, isolated hurricane force winds and
widespread hurricane force gusts will likely affect the southern
Peloponnese coasts and the Cyclades.
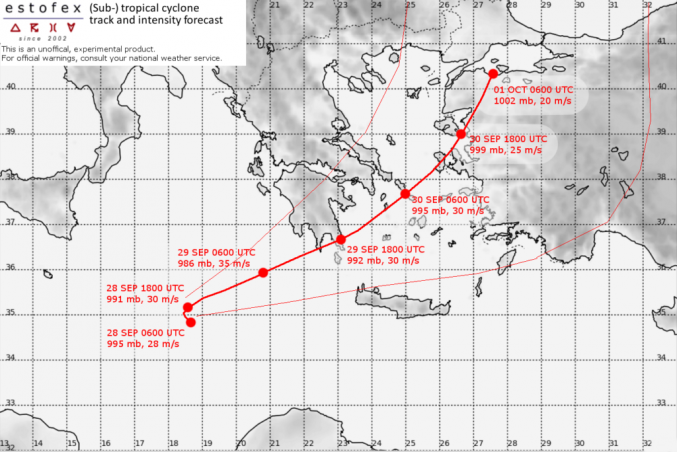
Forecast:
FH DATE & TIME LOCATION PRESSURE WIND MAX.GUSTS
00 28SEP 0600 UTC 34.8N 18.7E 995 mb 28 m/s 35 m/s
12 28SEP 1800 UTC 35.2N 18.6E 991 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s
24 29SEP 0600 UTC 35.9N 20.8E 986 mb 35 m/s 45 m/s
36 29SEP 1800 UTC 36.7N 23.1E 992 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s NEAR COAST
48 30SEP 0600 UTC 37.7N 25.0E 997 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s
60 30SEP 1800 UTC 39.0N 26.7E 999 mb 25 m/s 30 m/s AT COAST
72 01OCT 0600 UTC 38.8N 27.2E 1002 mb 20 m/s 25 m/s INLAND

Mesoscale Discussion
Valid: Fri 28 Sep 2018 09:00 to Fri 28 Sep 2018 21:00 UTC
Issued: Fri 28 Sep 2018 09:01
Forecaster: ESTOFEX
This is a Mesoscale Discussions issued for a cyclone
that is primarily driven by convection, issued twice daily before 9,
and 21 UTC until the cyclone dissipates or becomes extratropical. This
Mesocale Discussion is not an official producat and does not substitute
any warnings from National Meteorological Services. We welcome any
feedback at [email protected].
System: 2018M02
At 28 SEP 0600UTC the storm centre was located near 34.8N and 18.7E
Estimated minimum pressure: 995 mb.
Maximum sustained winds: 28 m/s (55 kt, 100 km/h).
Maximum gusts: 35 m/s (70 kt, 125 km/h).
ANALYSIS
Overnight,
the cyclone has organized and deepened, while drifting northward. Cloud
bands are spiralling around the intensified vortex, although a tight
inner circulation has not (yet) developed. A subjective Hebert-Poteat
technique estimate yields T numbers between 3.0 and 3.5 at 06 UTC,
supporting a minimum pressure of near 995 mb and maximum sustained winds
near 28 m/s.
FORECAST
Models are in agreement that the
cyclone should move only very slowly during the next 12 hours, before
accelerating east-northeastward towards the Peloponnese, as an upper
left trough approaches from the northwest. The greastest uncertainty in
the forecast is the extent of interaction with the mountainous region of
the Peloponnese: ICON and UKMO predicting the greatest interaction and
strongest weakening, whereas ECMWF and ARPEGE continue feature a more
southerly track with less influence on the inner core. The new track and
intensity forecast are a blend of these different solutions. The track
has been adjusted slightly to the south, and is quicker after 36 hours.
The forecast takes the cyclone into Northwestern Anatolia on Sunday
evening, upon which the cyclone will weaken rapidly.
The cyclone
is predicted to intensify somewhat more prior to landfall the
Peloponnese as suggsted by UKMO and ARPEGE, before moderate weakening
occurs. As said, the intensity forecast after 36 hours is strongly
dependent on the level of interaction with terrain and therefore rather
uncertain.
The primary hazard of the cyclone is expected to be very
heavy precipitation. Amounts of 200-300 mm can be expected on Saturday
and Sunday across the Peloponnese, 125-250 mm over Attica, Eastern
Central Greece (including Euboia) and the Cyclades, and 50–125 mm over
southern Crete, Western Anatolia, the North Aegean Islands and
Dodecanese Islands. In addition, isolated hurricane force winds and
widespread hurricane force gusts will likely affect the southern
Peloponnese coasts and the Cyclades.
Forecast:
FH DATE & TIME LOCATION PRESSURE WIND MAX.GUSTS
00 28SEP 0600 UTC 34.8N 18.7E 995 mb 28 m/s 35 m/s
12 28SEP 1800 UTC 35.2N 18.6E 991 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s
24 29SEP 0600 UTC 35.9N 20.8E 986 mb 35 m/s 45 m/s
36 29SEP 1800 UTC 36.7N 23.1E 992 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s NEAR COAST
48 30SEP 0600 UTC 37.7N 25.0E 997 mb 30 m/s 40 m/s
60 30SEP 1800 UTC 39.0N 26.7E 999 mb 25 m/s 30 m/s AT COAST
72 01OCT 0600 UTC 38.8N 27.2E 1002 mb 20 m/s 25 m/s INLAND
 http://www.meteociel.fr/observations-meteo/satellite.php?mode=animation-visible-special
http://www.meteociel.fr/observations-meteo/satellite.php?mode=animation-visible-specialVer em cima 'Spécial Medicane'
---
11:36z (ventos em nós)

Última edição:
2018  "Medicane", a tempestade rara que vai atingir a Grécia
"Medicane", a tempestade rara que vai atingir a Grécia
2017 Storm Numa May Become a Rare 'Medicane' in the Mediterranean Sea Late This Week
Storm Numa May Become a Rare 'Medicane' in the Mediterranean Sea Late This Week
2016 Watch this rare ‘medicane’ tropical storm take shape in the Mediterranean
Watch this rare ‘medicane’ tropical storm take shape in the Mediterranean
...
 "Medicane", a tempestade rara que vai atingir a Grécia
"Medicane", a tempestade rara que vai atingir a Grécia2017
 Storm Numa May Become a Rare 'Medicane' in the Mediterranean Sea Late This Week
Storm Numa May Become a Rare 'Medicane' in the Mediterranean Sea Late This Week2016
 Watch this rare ‘medicane’ tropical storm take shape in the Mediterranean
Watch this rare ‘medicane’ tropical storm take shape in the Mediterranean...
Storms in the Mediterranean Sea which exhibit some characteristics of a tropical cyclone are not particularly rare. The last example, in November 2017, produced flash flooding over parts of Greece. Similar storms also occurred in 2016 and 2014 bringing strong winds and heavy rain to Crete and Malta respectively.
lserpa
Cumulonimbus
Bem, daqui a dias temos que criar um tópico no seguimento tropical para o Mediterrâneo... nos últimos anos tem havido sempre 
Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk

Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
Danilo2012
Nimbostratus
lserpa
Cumulonimbus
A qual é voces devem estar de brincadeira 992hpa nao é nada! rs
Brother, o que interessa não é a profundidade da coisa, mas sim o diferencial isobárico... if you no what I mean
Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
Danilo2012
Nimbostratus
Of corse dude lol but im not seeing any really high pressure aroundBrother, o que interessa não é a profundidade da coisa, mas sim o diferencial isobárico... if you no what I mean
Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
lserpa
Cumulonimbus
1029 para 990hpa é um diferencial de quase 40mb, e o anticiclone está mesmo ali ao lado...
E há outros em redor que também ajudam à festa.
Relembro que os fluxos vão sempre das altas pressões para as baixas. Lei básica da física.

Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
E há outros em redor que também ajudam à festa.
Relembro que os fluxos vão sempre das altas pressões para as baixas. Lei básica da física.

Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
lserpa
Cumulonimbus
Belas ondas. Bonito de se ver, mas os prejuízos já vão surgindo...
Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk
Enviado do meu iPhone usando o Tapatalk